In an age where blockchain technology promises unparalleled security and decentralization, the thirst for interconnectivity among disparate blockchain networks continues to surge. Polkadot, a unique multi-chain framework, is poised at the forefront of this evolutionary leap, offering a promising solution through its cross-chain messaging protocol. The idea is bold and ambitious — to enable seamless communication and interoperability between independent blockchains, known as parachains. This article delves into the inner workings of cross-chain messaging in Polkadot, examining the infrastructure that could be the bedrock of the next generation of the interconnected blockchain ecosystem.
Bridging the Gap: Polkadot’s Vision

Polkadot emerges as a revolutionary platform designed to enable disparate blockchains to communicate and share value in a trust-free fashion. This interconnectedness is achieved through a sophisticated architecture that facilitates cross-chain messaging, allowing standalone networks to interact:
- Interoperability – The primary goal is to create a web of blockchains where information and transactions can be seamlessly exchanged.
- Scalability – By spreading transactions across multiple parallel chains, Polkadot aims to vastly improve network capacity and speed.
- Innovation Friendly – Developers are empowered to create specialized blockchains tailored to specific use cases, benefiting from the shared security and interoperability of the Polkadot ecosystem.
- User-Driven Governance – With an emphasis on stakeholder voted governance, Polkadot ensures that all voices can contribute to the future direction of the network.
The vision of Polkadot is not just to connect blockchains, but to facilitate the creation of an entirely decentralized web, laying the groundwork for a new era of collaborative innovation.
Anatomy of a Cross-Chain Message

Cross-chain messages in Polkadot are more than just information packets; they are the embodiment of interoperability and collaboration:
- Structure – Each message is structured to include sender and receiver information, the payload (or the actual information being sent), and a verification mechanism for security.
- Lifecycle – Messages are sent from a sender (originating blockchain), to the Relay Chain, and finally to the receiver (target blockchain), involving a series of protocol steps to ensure accuracy and security.
- Smart Contracts Integration – Cross-chain messages can trigger complex actions, such as executing smart contracts on the target chain, opening up a plethora of use cases.
- Fees – To prevent spam and misuse, these messages often incur a fee, payable in the native Polkadot token (DOT), which helps maintain the economic stability of the network.
A cross-chain message is like a digital envoy of the Polkadot network, capable of activating transactions, agreements, and applications beyond its native borders.
The Relay Chain Explained
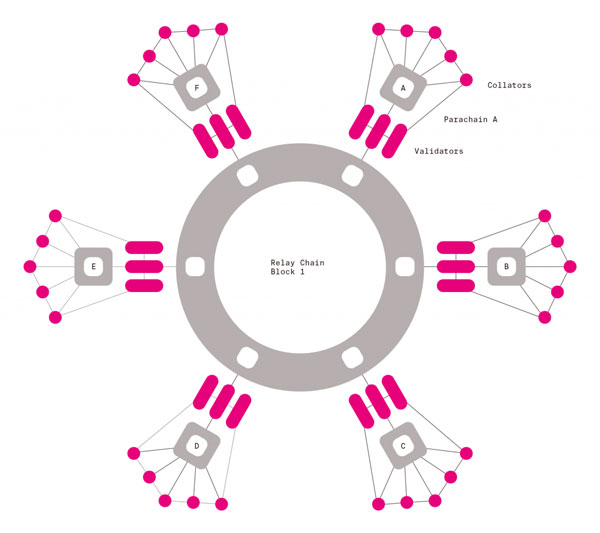
At the heart of Polkadot’s architecture is the Relay Chain, the main communication highway for cross-chain messages:
- Routing – The Relay Chain acts as the central coordinator, routing messages between various parachains and ensuring that they reach their intended destinations.
- Consensus – With its unique consensus algorithm, the Relay Chain handles the addition of new blocks to parachains while preserving network security and consistency.
- Finality – The technology ensures that once transactions are included in the chain, they are final and irreversible, instilling trust in the system’s integrity.
It is the robust foundation upon which Polkadot’s vision of a versatile, interconnected blockchain infrastructure is built, providing the essential toolkit for evolving the landscape of distributed ledger technology.
Parachains Interaction Dynamics

The interaction dynamics between parachains within Polkadot showcase the true potential of cross-chain messaging:
- Each parachain is a sovereign blockchain with its own tokens, rules, and governance, yet able to communicate with the broader network.
- Through Polkadot’s Cross-Consensus Message (XCM) format, parachute messages are standardized, ensuring compatibility and understanding across different chains.
- Parachains can also share computing resources, enabling otherwise resource-constrained networks to benefit from Polkadot’s pooled security and processing power.
Secure Messaging: The Security Model

The security model of cross-chain messaging in Polkadot is multifaceted, prioritizing integrity, availability, and confidentiality:
- Integrity – Cross-chain messages are cryptographically signed and validated, preventing unauthorized modification.
- Availability – The network is designed to remain operational even if individual components fail, ensuring that messages are not lost.
- Confidentiality – Messages may be kept private through encryption, allowing sensitive information to be securely transmitted across the ecosystem.
Polkadot approaches security holistically, ensuring each message is wrapped in robust, state-of-the-art safeguards, protecting the network from potential threats and ensuring trust among its participants.
Towards Interoperability: Future Steps

Polkadot’s current achievements in cross-chain messaging are just the beginning. Moving towards true interoperability involves continual development:
- Embracing New Standards – The ongoing refinement of protocols to accommodate evolving needs and technologies across blockchain ecosystems.
- Growth of the Ecosystem – As more parachains join the network, a richer tapestry of connectivity and possibility will emerge.
- Strengthening Governance – Ensuring the long-term viability of the network through transparent and responsive governance systems.
Polkadot’s journey is about iteration, adoption, and overcoming the technical challenges that come with pioneering such a transformative approach to blockchain interoperability.
| Feature | Relay Chain | Parachains |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Central hub | Sovereign blockchains |
| Communication | Facilitates cross-chain messaging | Sends and receives messages |
| Security | Pooled security | Benefit from Relay Chain’s security |
| Specialization | Provides consensus and finality | Tailored to specific use cases |
| Scalability | Orchestrates transaction validation | Independently processes transactions |
| Governance | Overseen by all Polkadot stakeholders | Individual governance structures |
Comparison Table: Relay Chain vs. Parachains Functions
The vision of a fully interoperable ecosystem of blockchains is not only becoming more tangible through platforms like Polkadot but is setting the stage for a new chapter in the evolution of blockchain technology. Cross-chain messaging is the crucial artery of this evolution, enabling independent chains to build strength through unity. As Polkadot continues to bridge the gaps between isolated networks, the future of blockchain is one that is both interconnected and boundlessly innovative. The road ahead is long, but the framework laid down by Polkadot’s architecture promises a journey marked by groundbreaking growth and collaboration.
