Polkadot, the heterogeneously sharded blockchain, is redefining the scalability and interoperability narrative in the cryptocurrency landscape. At its heart lies the Relay Chain, which functions as the main coordinator between various parallel blockchains, known as parachains. This article delves into the architecture of Polkadot’s Relay Chain, providing an in-depth understanding of its operational blueprint, consensus mechanisms, and the overarching role it plays in maintaining network coherence and high-level security. As the cornerstone of Polkadot’s innovative multi-chain structure, the Relay Chain is a testament to the network’s commitment to a more interconnected and adaptable blockchain future.
Polkadot’s Core: The Relay Chain

The Relay Chain is the central nervous system of the Polkadot network. Conceived by Dr. Gavin Wood, a cofounder of Ethereum, Polkadot presents a next-generation blockchain protocol that aims to create a fully functional and user-friendly decentralized web. The Relay Chain’s primary purpose is to ensure the seamless communication and interoperability of multiple blockchain shards – or parachains. It handles the network’s consensus, finality, and governance, leaving the parachains free to focus on specialized tasks without worrying about the underlying mechanics of a secure blockchain protocol.
Inside the Relay Chain, various components work in concert. Validators, the key players in the network, are responsible for maintaining the integrity of the network. They participate in consensus, validate proofs from parachains (cross-chain messages), and engage in governance. Nominators, on the other hand, delegate their stake to trustworthy validators, contributing to the overall security of the network. Then there are collators, who assist by collecting parachain transactions and producing proofs for validators. Last in the list are fishermen, entities that monitor the network and report bad behavior to validators.
At every level, the Relay Chain’s design emphasizes maximal simplification. It does not natively support smart contracts to maintain its role as a clean, efficient coordinator between parachains. It’s a stark contrast from parachains which can be customized with a wide array of features suited to their specific needs. Instead, the Relay Chain is focused on process transactions as quickly and securely as possible, essentially delegating complexity to the parachains to streamline its own operations.
Handling such a wide range of responsibilities, the Relay Chain facilitates communication between the different parachains, even those with wildly different architectures. Through the Relay Chain, Polkadot ensures that its vision of a ‘multi-chain’ network is not only technically feasible but also efficient and secure. Polkadot’s sharded model allows each parachain to handle its own transactions, which are then finalized on the Relay Chain in a way that they are interoperable with other parachains.
Inside Relay Chain: How it Works
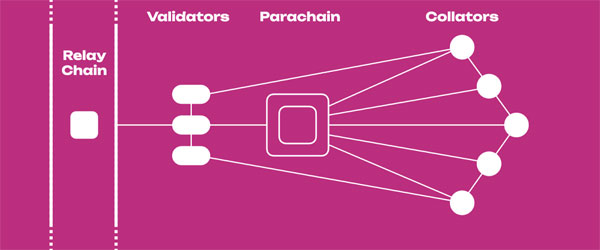
The Relay Chain is a complex system, but a closer look reveals a finely-tuned machine that meticulously bridges different blockchain networks. Here’s how it unfolds:
- Collation Gathering: Collators on individual parachains bundle transactions into a set. These are essentially candidate blocks that could be added to the Relay Chain.
- Consensus Formation: Validators on the Relay Chain take these collected transactions from collators and participate in a consensus protocol to agree on the validity and ordering of the transactions, creating consensus candidate blocks.
- Block Production: Validators create and propose blocks to be added to the Relay Chain, incorporating proofs from the collators’ curated transactions.
- Finality Voting: Using a sophisticated consensus algorithm, validators participate in a finality-gadget voting protocol that finalizes the blocks.
- Cross-Chain Messaging: The Relay Chain processes messages sent between different parachains, ensuring that the entire network can communicate effectively.
The intricacies involved in operating the Relay Chain are carefully orchestrated, ensuring a balance between efficiency, speed, and security.
Consensus Mechanisms Unveiled

Polkadot employs a combination of two consensus mechanisms to secure its network:
- Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS): This serves as the primary mechanism. Validators are selected based on the stake behind them (their own plus what’s nominated by the nominators). This discourages malicious behavior due to the economic stakes involved.
- GRANDPA (GHOST-based Recursive ANcestor Deriving Prefix Agreement): This mechanism is responsible for finalizing blocks. It allows the network to come to an agreement on the best chain and finalize multiple blocks at once, which significantly increases the speed of the chain.
This hybrid model not only ensures robust security but also fosters network efficiency and reduces the time taken to reach consensus on the state of the blockchain.
Relay Chain’s Role in Interconnectivity

The Relay Chain’s primary role in Polkadot’s architecture is to facilitate interoperability and interconnectivity among the various parachains. It does this through:
- Cross-Chain Message Passing (XCMP): This protocol allows parachains to communicate with one another through the Relay Chain by exchanging messages.
- Shared Security Model: Parachains benefit from the pooled security of the entire network. The Relay Chain validators validate the transactions of all parachains, adding an extra layer of security.
- Network Governance: Through a sophisticated governance model, the Relay Chain coordinates upgrades and changes across the network without the need for hard forks.
This glue-like functionality ensures that, although parachains operate independently, they can work together as part of a larger, interconnected ecosystem.
Ensuring Security on the Relay Chain
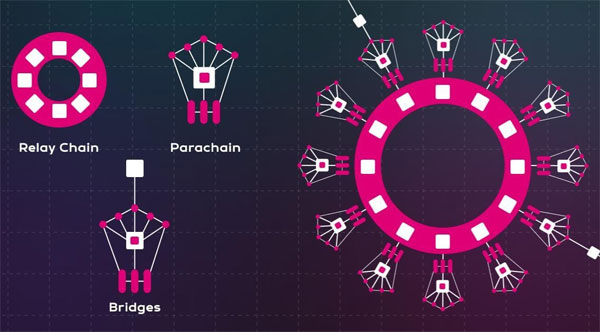
Security is a critical element within Polkadot’s framework, and the Relay Chain takes center stage in this regard:
- Validator Election: By using NPoS, the network selects validators with large amounts of staked DOT, the native currency, which aligns their interests with the network’s integrity.
- Economic Punishments (Slashing): Validators or nominators who act maliciously or fail to perform their duties correctly are punished by “slashing,” where a portion of their staked DOT is destroyed.
- Fishermen: These play an essential role in Polkadot’s layered security architecture. They look out for misconduct and stand to receive a reward for successful identification of malevolence.
These mechanisms provide a highly secure environment that significantly reduces the possibility of attacks like double-spends or chain reorganizations.
Future-Proofing with Polkadot Relay
Polkadot’s vision for a scalable and interoperable blockchain ecosystem is directly tied to the versatility and capability of the Relay Chain. The architecture is designed to adapt to an evolving landscape through:
- Upgradability: The Polkadot network can upgrade without hard forks, allowing for a growth trajectory that is as seamless as it is powerful.
- Substrate Framework: Parachains use Substrate to create custom blockchains that are inherently compatible with the Relay Chain, aiding in an ecosystem of diverse but interconnected chains.
- Onboarding of New Parachains: The Relay Chain is prepared to accommodate an expanding network of parachains, increasing the network’s capacity and capabilities.
The design and implementation of the Relay Chain position it as a scalable and adaptable foundation for cross-chain integration within the Polkadot ecosystem.
Comparison Table: Relay Chain vs. Parachains
| Feature | Relay Chain | Parachains |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Coordination, Consensus, and Security | Specialized Transaction Processing |
| Smart Contract Support | No | Yes (Varies by Parachain) |
| Validator Role | Validators work only on the Relay Chain | Collectors work on specific parachains |
| Security | Shared Security Model | Inherits security from the Relay Chain |
| Upgradability | Network upgrades without hard forks | Independent upgrades |
| Interoperability Protocol | Cross-Chain Message Passing (XCMP) | Rely on Relay Chain for messaging |
Through the Relay Chain, Polkadot establishes a blueprint for the future of blockchain interoperability and scalability. The ingenuity behind its architecture underlies a system built for secure, efficient consensus and cross-chain communication, magnifying the potential of the entire network. As blockchain technology continues to mature, the Relay Chain stands out with its robust and forward-thinking framework, destined to play a pivotal role in the evolution of the decentralized web. In a world where collaboration is key, Polkadot’s Relay Chain paves the way for truly interconnected blockchain ecosystems.
