In an era where blockchain technology is rapidly evolving, Polkadot stands out as a multifaceted network that aims to solve the pressing issue of scalability — a challenge that has proven to be a significant hurdle for legacy blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum. This article delves into the technical intricacies of Polkadot’s architecture, offering insights into how this next-generation blockchain protocol is not just addressing scalability but also interoperability, enabling a diverse range of blockchains to communicate and interact seamlessly.
Breaking Down Polkadot’s Network

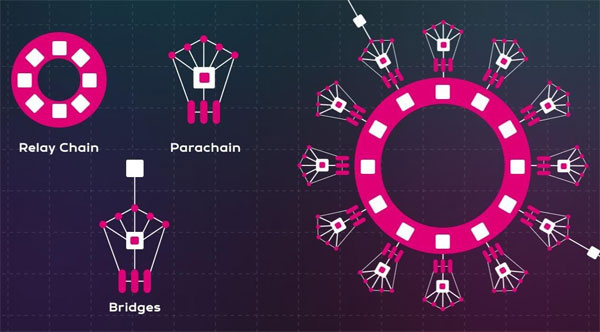
Polkadot’s network is an interconnected web of individual blockchains, each designed to serve a specific purpose within the ecosystem. At its core, this network is structured to allow for continuous expansion and flexibility, while maintaining security and the ability to process numerous transactions simultaneously. Here’s a detailed look at the components that make Polkadot’s network unique:
- The Relay Chain acts as the heart of Polkadot, responsible for the network’s shared security, consensus, and cross-chain interoperability.
- Parachains are individual blockchains that run in parallel, each optimized for their unique functionalities while leveraging the Relay Chain’s security and connectivity.
- Parathreads are similar to parachains, but with a pay-as-you-go model that is optimal for less frequently used or smaller-scale blockchains.
- Bridges enable connections between Polkadot and external networks like Ethereum and Bitcoin, allowing for the transfer of tokens and information across different blockchain systems.
This multi-layered structure is the bedrock upon which Polkadot achieves its scalability, with each layer playing a pivotal role in the overall performance of the network.
Polkadot’s Parachains Explained

Parachains are at the forefront of Polkadot’s scalability solutions. As specialized blockchains, they are tailored for various use cases — from DeFi to smart contracts, and more — operating in parallel to avoid the bottlenecks associated with traditional blockchain networks. Each parachain has distinct features:
- Customizability: Parachains can be uniquely designed with specific features to meet project requirements.
- Shared Security: By connecting to the Relay Chain, parachains enjoy collective security without the need to establish their isolated set of validators.
- Specialized Processing: Parachains can process transactions and operations that are optimized for their specific application, facilitating efficiency and speed.
- Auction Mechanism: Slot spaces for parachains on the Relay Chain are obtained through auctions, promoting a fair and open process.
- Limited Slots: There is a cap on the number of parachain slots to ensure performance and security, which makes obtaining a slot competitive.
- Parathread Option: For projects that may not need a continuous connection to the Relay Chain, the more economical parathread option offers a flexible alternative.
Parachains form a crucial piece in the scalability puzzle by distributing the workload across the entire network, preventing any single point from becoming a bottleneck.
Relay Chain: Polkadot’s Backbone
The Relay Chain is the foundational layer of Polkadot’s network, providing several critical functions:
- Ensuring Network Consensus: Validators on the Relay Chain are responsible for adding new blocks to the parachains and validating the information.
- Handling Cross-Chain Transfers: It acts as an intermediary for transferring messages, including transactions, between parachains.
- Enforcing Shared Security: The Relay Chain’s pooled security model protects parachains from potential attacks.
- Enabling Parachain Auctions: It manages the non-permanent leasing of parachain slots via auctions.
- Coordination of Network Upgrades: By managing upgrades for the whole ecosystem, the Relay Chain allows Polkadot to evolve without hard forks.
- Finalization of Blocks: It employs the GRANDPA algorithm to finalize blocks across all parachains, enabling consistent and reliable transaction settlement.
As the central coordinator, the Relay Chain is critical to Polkadot’s ability to scale and secure a heterogeneous network of specialized blockchains.
Cross-Chain Interoperability

Interoperability is another significant aspect where Polkadot excels; it’s built into the DNA of the network. This cross-chain communication is facilitated by several mechanisms:
- XCMP: The Cross-Chain Message Passing protocol allows parachains to send messages to each other, including information and tokens.
- SPREE: Shared Protected Runtime Execution Enclaves ensure that specific code across different parachains behaves identically when handling cross-chain messages.
- Bridges: These special blockchains connect Polkadot with other chains like Ethereum, allowing for asset transfers and information sharing.
- Relay Chain’s Role: It coordinates the consensus of cross-chain transactions and asserts finality.
- Trust-Free Environment: The design of inter-chain communication does not rely on trust assumptions, maximizing the security of inter-operability.
- This comprehensive model of interoperability bolsters scalability by allowing diverse blockchains to offload certain processes to other parachains better suited to deal with them.
Scaling via Substrate Framework

Substrate is the bedrock development framework enabling creators to build custom blockchains from scratch. It is central to Polkadot’s scalability in several ways:
- Modular Design: Developers can pick and choose the components they need, resulting in lean, purpose-built blockchains.
- Innate Compatibility: Substrate-based blockchains are inherently compatible with Polkadot, which streamlines the integration into the network.
- Upgradeability: The ability of Substrate blockchains to upgrade without hard forks helps maintain operational continuity and scalability.
- Robust Developer Community: A rich ecosystem of developers contributes to Substrate, ensuring a constant infusion of innovative solutions for scalability.
- Rapid Deployment: Substrate significantly reduces the development time and effort, accelerating the growth of the Polkadot network.
- Rust Programming Language: Substrate’s reliance on Rust offers a balance between speed and safety, emphasizing the performance aspect of scalability.
The scalability of Polkadot hinges not just on the network design itself but also on the capabilities and ease of development that Substrate provides, fostering a fertile ground for innovation and growth.
Future-Proofing via NPoS

Nomination Proof of Stake (NPoS) is Polkadot’s adjusted consensus mechanism, aiming to secure the network and facilitate scalability:
- Maximizing Security: NPoS is designed to elect a large number of validators, enhancing the security and resilience of the network.
- Staking Economy: This consensus mechanism encourages a healthy staking economy with incentives for nominators and validators.
- Adaptability: NPoS can adjust dynamically to network conditions, which optimizes processing power and security.
- Decentralization: It promotes a more egalitarian distribution of power among validators and nominators.
- Energy Efficiency: Compared to traditional Proof of Work mechanisms, NPoS is significantly more energy-efficient.
- Strong Governance: The on-chain governance system integrated with NPoS allows a streamlined process for making consensus changes when necessary.
NPoS gives Polkadot a mechanism that is state-of-the-art in securing a decentralized network and is engineered to support scaling without compromising on performance or robustness.
Comparison Table: Scalability Solutions Across Blockchain Protocols
| Feature | Polkadot | Ethereum 2.0 | Bitcoin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parachains | Yes (Specialized blockchains) | No | No |
| Shared Security | Yes (Relay Chain) | Yes (Beacon Chain) | No |
| Cross-Chain Messaging | Yes (XCMP/SPREE/Bridges) | Future Upgrades (Shards) | No |
| Upgradeability | Yes (No hard forks needed) | Yes (via Beacon Chain) | No (Requires hard forks) |
| Consensus Mechanism | NPoS (Nominated Proof of Stake) | PoS (Proof of Stake) | PoW (Proof of Work) |
| Developer Framework | Substrate | Solidity/Vyper | Bitcoin Script |
Polkadot’s multifaceted approach to scalability and interoperability contrasts sharply with the “one-size-fits-all” blockchains of the past. By exploring the technical foundations, from its Relay Chain and parachain architecture to the innovative Substrate development framework and NPoS consensus, Polkadot presents itself as a compelling solution that doesn’t just address current scalability issues but also paves the way for futuress expansion and integration. With these mechanisms in place, Polkadot is well on its way to enabling a more interconnected, efficient, and scalable blockchain ecosystem for the decentralized web of tomorrow.
